Understanding Dog Fight Bite Wounds and Surgical Interventions
Dog fights can result in serious injuries, requiring immediate medical attention to prevent complications like infections, tissue damage, and long-term mobility issues. At the Veterinary Emergency and Specialty Center of Northern Arizona, our team specializes in handling emergency cases, including severe bite wounds that may require surgical intervention.
This guide covers how to identify serious bite wounds, when surgery is necessary, and how to care for your pet post-treatment to ensure a successful recovery.
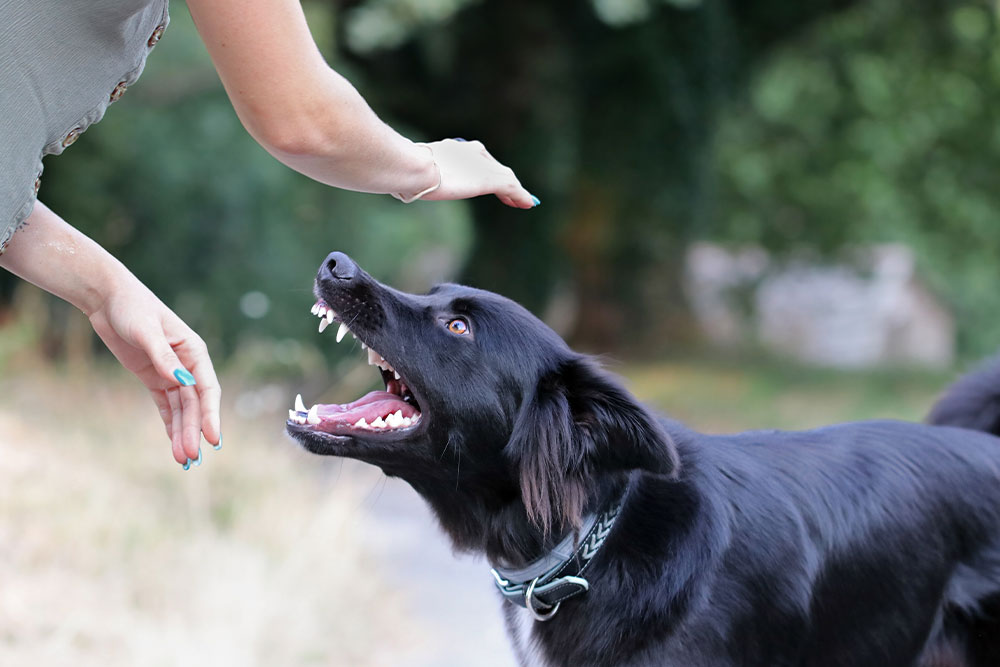
Understanding Canine Aggression and Injuries
Dogs may engage in fights for various reasons, including:
- Territorial disputes over space or resources
- Fear-based aggression when feeling threatened
- Overstimulation during play that escalates into a fight
- Defensive aggression in response to an unfamiliar or aggressive dog
Regardless of the cause, dog fights can result in deep puncture wounds, lacerations, and even internal injuries, making immediate veterinary evaluation critical. The severity of wounds is not always visible, as bite injuries can cause underlying tissue trauma that worsens without treatment.
Recognizing Serious Bite Wounds: When to Seek Veterinary Care
Bite wounds vary in severity, from minor scratches to deep punctures that affect muscles, bones, and organs. Bites are rarely a simple puncture; since a dog bite is typically “bite and shake” or “bite and tug”, there is almost always deeper damage. Seek immediate veterinary care if you notice:
- Excessive bleeding that does not stop within a few minutes
- Deep wounds with torn or separated skin
- Signs of shock, including pale gums, rapid breathing, or weakness
- Swelling or pus, which can indicate infection
- Limping or reluctance to move, suggesting muscle or joint damage
Even small puncture wounds can become infected quickly due to bacteria from a dog’s mouth. Delaying treatment can lead to abscesses, necrosis, and systemic infections.
The Role of Surgery in Treating Severe Bite Wounds
Surgical intervention is often necessary when bite wounds involve:
- Deep punctures affecting muscles or tendons
- Significant skin tearing requiring sutures or reconstructive surgery
- Infections or abscesses needing debridement and drainage
Key Surgical Procedures for Bite Wounds
- Debridement – Removal of dead or infected tissue to promote healing
- Suturing & Wound Closure – Aligning tissues to minimize scarring and speed up recovery
- Drain Placement – Preventing fluid accumulation that could lead to abscess formation
- Reconstructive Surgery – For severe wounds requiring skin grafts or flap procedures
Each case is unique, and our veterinarians will determine the best course of action based on wound severity and infection risk.
Read more about bite wound management from the AKC.
Post-Surgical Care: Ensuring a Smooth Recovery
Immediate Aftercare
After surgery, proper wound management is essential to prevent infection and delayed healing. Your veterinarian may recommend:
- Pain management – Prescribed medications to keep your pet comfortable
- Antibiotics – To prevent bacterial infections in deep wounds
- Restricted activity – Limiting movement to allow proper healing
- Elizabethan collar (E-collar) – To prevent licking or scratching at the wound
Signs of Complications
Monitor for these signs and contact your veterinarian if they occur:
- Increased swelling, redness, or pus discharge
- Foul odor from the wound
- Lethargy, fever, or decreased appetite
- Wound opening or excessive bleeding
Preventing Dog Fights and Future Injuries
While some fights are unavoidable, pet owners can take steps to reduce the risk of aggressive encounters.
Strategies for Preventing Dog Fights
- Early socialization – Expose your dog to a variety of environments, animals, and people
- Recognizing warning signs – Growling, stiff posture, and intense staring are signs of aggression
- Avoid high-risk situations – Keep your dog leashed in unfamiliar areas and introduce new dogs gradually
- Provide training & behavioral support – Professional trainers can help address fear-based or resource-guarding aggression
Frequently Asked Questions About Dog Bite Wounds
1. What are the costs associated with bite wound surgery?
Costs vary based on wound severity, treatment complexity, and post-operative care. Veterinary financing options and pet insurance can help manage unexpected costs.
2. How long does recovery take after bite wound surgery?
Mild cases may heal within 10 to 14 days, while severe wounds requiring reconstructive surgery may take several weeks to months. Regular check-ups ensure proper healing.
3. What should I do if my dog is bitten outside of clinic hours?
Clean the wound with warm saline or diluted antiseptic, apply gentle pressure to control bleeding, and seek emergency care immediately.
Learn about emergency wound care.
Seeking Immediate Care for Dog Bite Injuries
Dog fights can happen unexpectedly, but fast action and professional veterinary care can prevent life-threatening complications. If your pet has suffered a bite wound, do not wait for symptoms to worsen—seek immediate veterinary attention.
At Veterinary Emergency and Specialty Center of Northern Arizona, we specialize in trauma care and surgical interventions to ensure your pet’s health and safety.







Leave A Comment